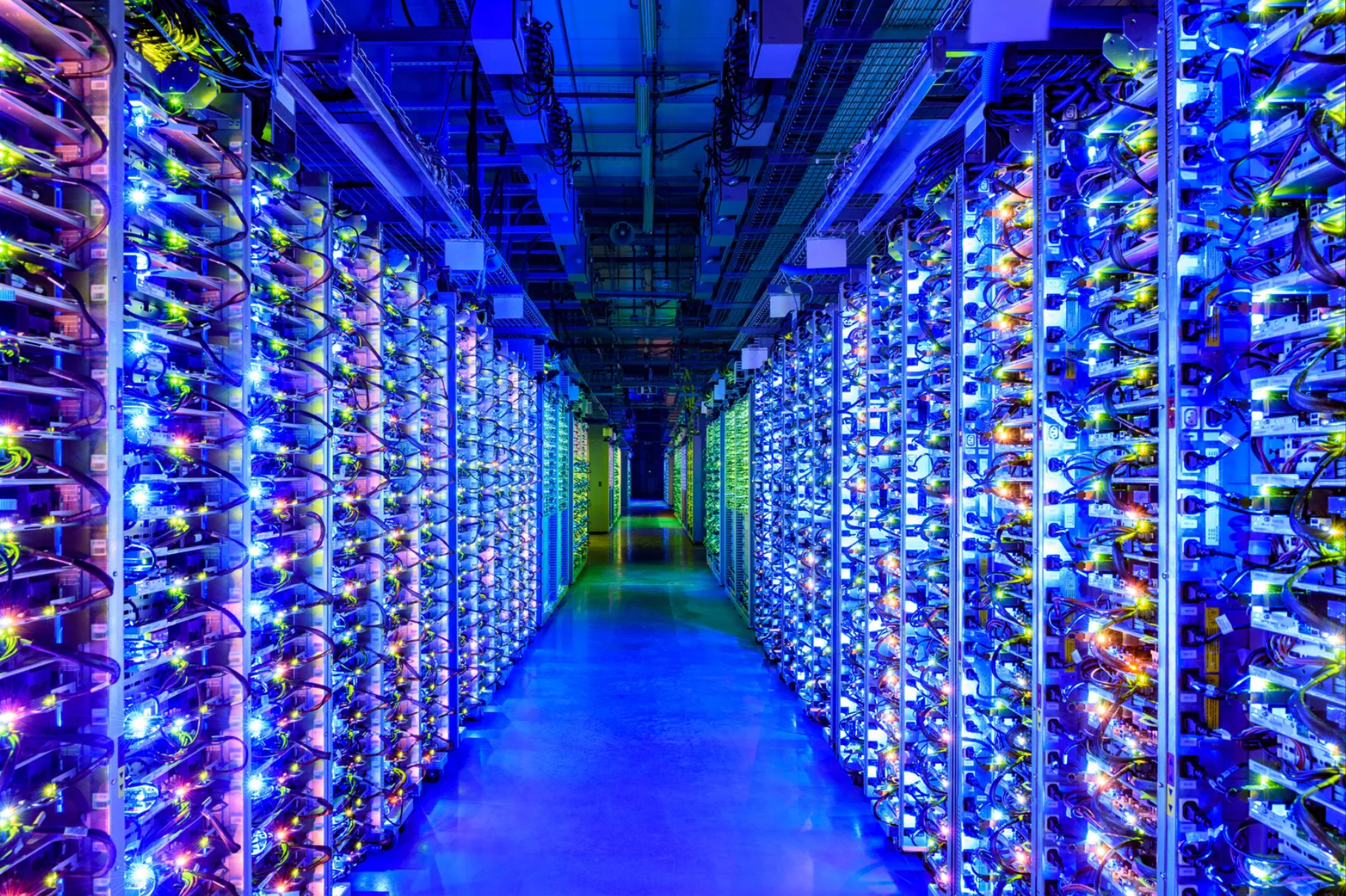
In this digitization era, businesses are inundated with vast amounts of data daily. Storing this information is essential, but protecting it from loss or damage is equally crucial. In the surge of cloud storage, tape backup stands as a cost-effective and secure approach to safeguarding valuable data.
Tape Backup:
Tape backup, though age-old, offers unmatched reliability, cost-effectiveness, and durability in data storage. Its advantages surpass contemporary storage methods in several aspects:
- Cost-Effectiveness: Compared to solid-state drives (SSDs) or hard disk drives, tape storage backup emerges as a more economical choice for bulk data storage. The high storage density and reusability make it a cost-efficient solution.
- High Capacity and Scalability: The latest tapes, like LTO 9, boast massive storage capacities, allowing up to 45 terabytes of uncompressed data. The linear scalability of tape backup enables easy expansion by adding more tapes.
- Durability and Longevity: Tapes exhibit impressive durability and can endure for up to thirty years when stored under optimal conditions.
- Reliable Disaster Recovery: Tape backup serves as a secure disaster recovery option, offering a fallback strategy in the event of cyberattacks or natural calamities.
Evolving Tape Backup Technology
The evolution of tape backup technology has transformed it from early reels to today’s advanced cartridge-based tapes. Advancements include increased storage capacities, faster data transfer rates, encryption features, and compliance with regulations like GDPR or HIPAA.
Despite the surge in cloud storage adoption, tape backup remains pivotal in data storage strategies, particularly in:
- Hybrid Cloud Environments: Providing an added layer of security and redundancy.
- Legal Compliance: Essential for maintaining records, ensuring compliance, and mitigating legal complications.
The Unmatched Role of Tape Backup:
Amidst the plethora of storage options, tape backup prevails as a reliable, cost-efficient, and secure means of safeguarding critical data for future use. Its longevity and unique advantages position it as an invaluable choice in the realm of modern data storage.
Applications and Industry Adaptations
- Healthcare and Finance: Sectors governed by strict regulations rely on tape backup to securely store sensitive information. Tape cartridges offer encryption, ensuring only authorized access.
- Large Enterprises: For organizations with extensive data archives, tape backup serves as a dependable, long-term storage solution. Its ability to store vast amounts of data for extended periods meets compliance needs.
- Disaster Recovery: Tape backup plays a pivotal role in disaster recovery strategies. Businesses deploy a 3-2-1 fallback strategy—two copies of data stored on-site and one off-site—ensuring robust data recovery in emergencies.
Benefits:
1. Environmental Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
Amid escalating concerns about environmental impact, Tap Backup champions sustainability. Unlike power-hungry data centers that demand substantial energy consumption for operation, tape backup systems exhibit unparalleled energy efficiency. With tapes being offline when not in use, they necessitate minimal power, contributing to reduced carbon footprints and aligning with eco-conscious initiatives.
2. Air-Gap Security: Shielding Against Cyber Threats
Tape backup’s offline nature provides an inherent air-gap security advantage, acting as an impervious barrier against cyber threats like ransomware and malware attacks. As tapes are physically disconnected from networks when not in use, they remain immune to online infiltrations, ensuring data integrity and protection against evolving cyber vulnerabilities.
3. Immutable Data Preservation for Compliance Needs
In an era rife with stringent data privacy regulations, tape backup emerges as an immutable data preservation solution. With Write Once, Read Many (WORM) functionalities, tapes ensure data immutability, addressing compliance requirements mandated by legislation like GDPR or HIPAA. This feature prevents unauthorized alterations or deletions, preserving the integrity of sensitive information.
4. Long-Term Accessibility and Data Legibility
Contrary to certain digital storage mediums susceptible to technological obsolescence or compatibility issues, tape backup assures long-term accessibility and data legibility. With backward compatibility and tape drive support extending over generations, accessing archived data remains feasible, safeguarding against format- or technology-related obsolescence challenges.
5. Reduced Data Center Footprint and Space Optimization
Tape backup drive compact physical footprint lends itself well to space optimization strategies within data centers. The condensed size of tapes in comparison to bulky server arrays or racks allows for more efficient space utilization, reducing storage complexities, and enhancing overall operational efficiency.
6. Offline Data Isolation for Privacy and Confidentiality
Tape backup’s offline state inherently isolates sensitive data from online exposure, ensuring privacy and confidentiality. This isolation shields critical information from potential breaches, providing an added layer of protection in compliance with privacy laws and regulations governing sensitive data handling.
7. Archiving and Preservation of Legacy Data Formats
For industries reliant on legacy data formats or proprietary systems, tape backup serves as a time-tested solution for archiving and preserving such data. This capability safeguards historical information, ensuring its accessibility and longevity, which is crucial for organizations reliant on legacy systems for specific operations or compliance needs.
8. Facilitating Secure Data Repatriation from Cloud Storage
In scenarios necessitating data repatriation from cloud environments due to shifting business needs or cost considerations, tape backup offers a secure and cost-efficient method for data retrieval. Facilitating seamless data migration from the cloud to on-premises storage, tapes ensure data availability without incurring exorbitant bandwidth or egress charges.
Challenges and Mitigations
While tape backup poses certain challenges—limited capacity, slower transfer speeds, higher costs, and prolonged data restoration—strategic approaches like compression algorithms, indexing systems, and optimized backup strategies help overcome these limitations.
Contrary to predictions of its demise, tape backup continues to evolve. With ongoing technological advancements, modern tape solutions integrate features like Write Once, Read Many (WORM) and Linear Tape File System (LTFS), further enhancing their usability and compliance capabilities.
Conclusion
As businesses navigate the ever-evolving landscape of data storage, the significance of tape backup remains resilient. Its cost-effectiveness, durability, and reliability make it an indispensable asset in comprehensive data storage strategies.
By embracing the enduring qualities of tape backup amidst rapid technological advancements, businesses ensure a robust, secure, and cost-efficient approach to preserving and accessing critical data.
Read more: What is the Role of DDR5 Memory Slots in AMD Servers?