Introduction
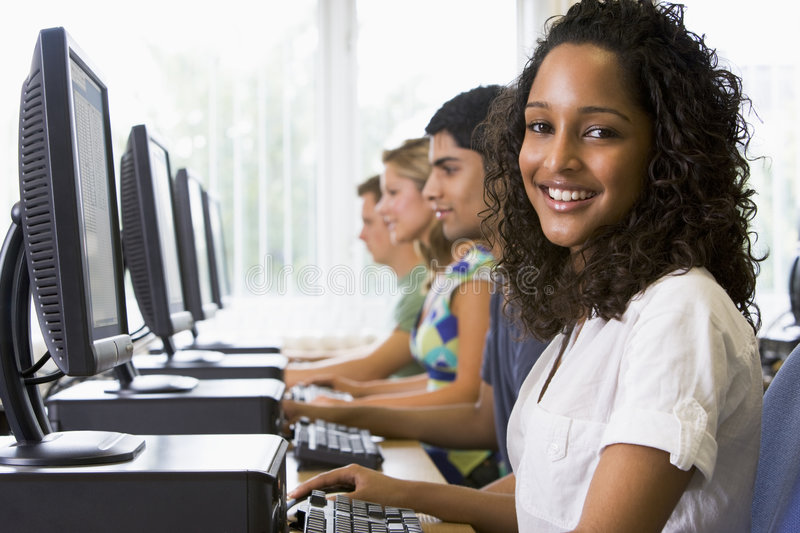
Nursing is a profession anchored in care, compassion, and an unwavering commitment to patient welfare. At the heart of nursing practice lies the concept of accountability, which compels nurses to operate within specific ethical and legal frameworks. This article delves into the Review the role of the nurse as an accountable practitioner within relevant ethical and legal frameworks , exploring how they navigate the complexities of ethical guidelines and legal regulations in their daily practice.
Understanding Accountability in Nursing
Accountability in nursing refers to the responsibility of nurses to deliver safe and effective care while adhering to established standards and regulations. This encompasses not only their actions but also their decision-making processes and the outcomes of their care. Nurses are expected to:
- Adhere to professional standards: This includes following protocols and guidelines established by healthcare institutions and professional bodies.
- Engage in continuous education: Lifelong learning is essential to remain updated on best practices and emerging health issues.
- Demonstrate ethical behavior: Nurses must navigate moral dilemmas and make decisions that prioritize patient welfare.
In essence, accountability is about owning one’s actions and their consequences, fostering trust and safety in the healthcare environment.
Ethical Frameworks in Nursing Practice
3.1 Principles of Biomedical Ethics
Biomedical ethics provide a foundational framework for ethical decision-making in healthcare. The four core principles include:
- Autonomy: Respecting a patient’s right to make informed decisions about their care.
- Beneficence: Acting in the best interest of the patient to promote their well-being.
- Non-maleficence: The obligation to avoid causing harm to patients.
- Justice: Ensuring fair and equitable treatment for all patients.
These principles guide nurses in delivering care that respects patients’ rights while ensuring ethical standards are met.
3.2 The Nursing Code of Ethics
The Nursing Code of Ethics, developed by the American Nurses Association (ANA), outlines the ethical obligations of nurses. Key provisions include:
- Respect for human dignity: Nurses must treat all patients with dignity and respect.
- Commitment to the patient: The patient’s well-being is the primary concern.
- Advocacy: Nurses are expected to advocate for patients’ rights and needs.
This code serves as a critical reference point for nurses, guiding their ethical practice and reinforcing their accountability.
Legal Frameworks Governing Nursing
4.1 Nursing Licensure and Regulations
Nurses must hold a valid nursing license to practice legally. Each state has its own Board of Nursing, which sets forth the regulations governing nursing practice. Key aspects include:
- Licensure exams: Nurses must pass the NCLEX-RN or NCLEX-PN to obtain licensure.
- Continuing education: Many states require ongoing education to maintain licensure.
- Scope of practice: Defined roles and responsibilities dictate what actions nurses are legally permitted to perform.
Compliance with these regulations is essential for protecting patient safety and maintaining professional accountability.
4.2 Malpractice and Liability
Malpractice refers to the failure of a healthcare professional to provide the standard of care, resulting in harm to the patient. For nurses, this can include:
- Negligence: Failing to act in accordance with established nursing standards.
- Failure to communicate: Not providing crucial information to other healthcare team members or patients.
- Inadequate documentation: Poor record-keeping that could compromise patient safety.
Understanding legal liability is crucial for nurses, as it underscores the importance of accountability in their practice.
The Intersection of Ethics and Law in Nursing
While ethics and law are distinct, they often intersect in nursing practice. Ethical principles can inform legal standards, and legal obligations can dictate ethical behavior. For example:
- A nurse may face an ethical dilemma when a patient refuses treatment that is legally mandated. In such cases, understanding both the ethical implications and legal requirements is essential for making informed decisions.
Navigating this intersection requires a strong understanding of both ethical principles and legal obligations, allowing nurses to uphold their accountability in diverse situations.
Accountability in Practice: Case Studies
Case Study 1: Medication Administration Error
A nurse administers the wrong medication to a patient. The ethical responsibility to do no harm (non-maleficence) and the legal requirement to adhere to medication protocols come into play. This situation highlights the importance of accountability in recognizing errors, reporting them, and taking corrective action.
Case Study 2: Patient Advocacy
A nurse advocates for a patient’s right to receive necessary treatment despite hospital policies. This scenario emphasizes the ethical obligation to respect patient autonomy and the legal protections available to patients.
Challenges in Maintaining Accountability
Despite the frameworks in place, nurses face several challenges in maintaining accountability, including:
- High workload: Increased patient-to-nurse ratios can lead to errors and oversight.
- Lack of support: Insufficient institutional support can hinder nurses’ ability to uphold ethical and legal standards.
- Conflicting demands: Navigating between patient needs, institutional policies, and legal regulations can create dilemmas.
Addressing these challenges is crucial for ensuring that nurses can fulfill their roles as accountable practitioners.
Strategies for Upholding Accountability
To maintain accountability, nurses can implement several strategies:
- Regular training: Participating in ongoing education and training to stay updated on best practices and legal requirements.
- Peer collaboration: Working collaboratively with colleagues to share knowledge and support ethical decision-making.
- Effective communication: Open dialogue with patients and healthcare teams can prevent misunderstandings and promote accountability.
By actively engaging in these practices, nurses can enhance their accountability and improve patient outcomes.
FAQs
What does accountability mean in nursing?
Accountability in nursing refers to the obligation of nurses to take responsibility for their actions and decisions, ensuring they provide safe and effective care while adhering to ethical and legal standards.
How do ethical frameworks influence nursing practice?
Ethical frameworks guide nurses in making decisions that prioritize patient welfare, uphold dignity, and navigate moral dilemmas while adhering to professional standards.
What are the legal responsibilities of nurses?
Nurses are legally responsible for providing care within their scope of practice, maintaining patient confidentiality, obtaining informed consent, and following established protocols and regulations.
How can nurses uphold accountability in challenging situations?
Nurses can uphold accountability by engaging in continuous education, collaborating with peers, and effectively communicating with patients and healthcare teams to make informed decisions.
Why is it important for nurses to understand the intersection of ethics and law?
Understanding the intersection of ethics and law enables nurses to navigate complex situations, ensuring that they uphold both ethical standards and legal obligations in their practice.
Conclusion
The role of the nurse as an accountable practitioner is crucial to the integrity of the healthcare profession. By navigating ethical and legal frameworks, nurses not only ensure the safety and well-being of their patients but also uphold the standards of their profession. As healthcare continues to evolve, so too will the challenges and responsibilities faced by nurses. Commitment to accountability, continuous education, and ethical practice will be essential in meeting these demands and providing high-quality care. Ultimately, nurses play a vital role in fostering trust within the healthcare system, ensuring that patients receive the care they deserve within a framework of accountability.