The Art and Science of Metal Forging: How Modern Facilities Shape Forged Parts
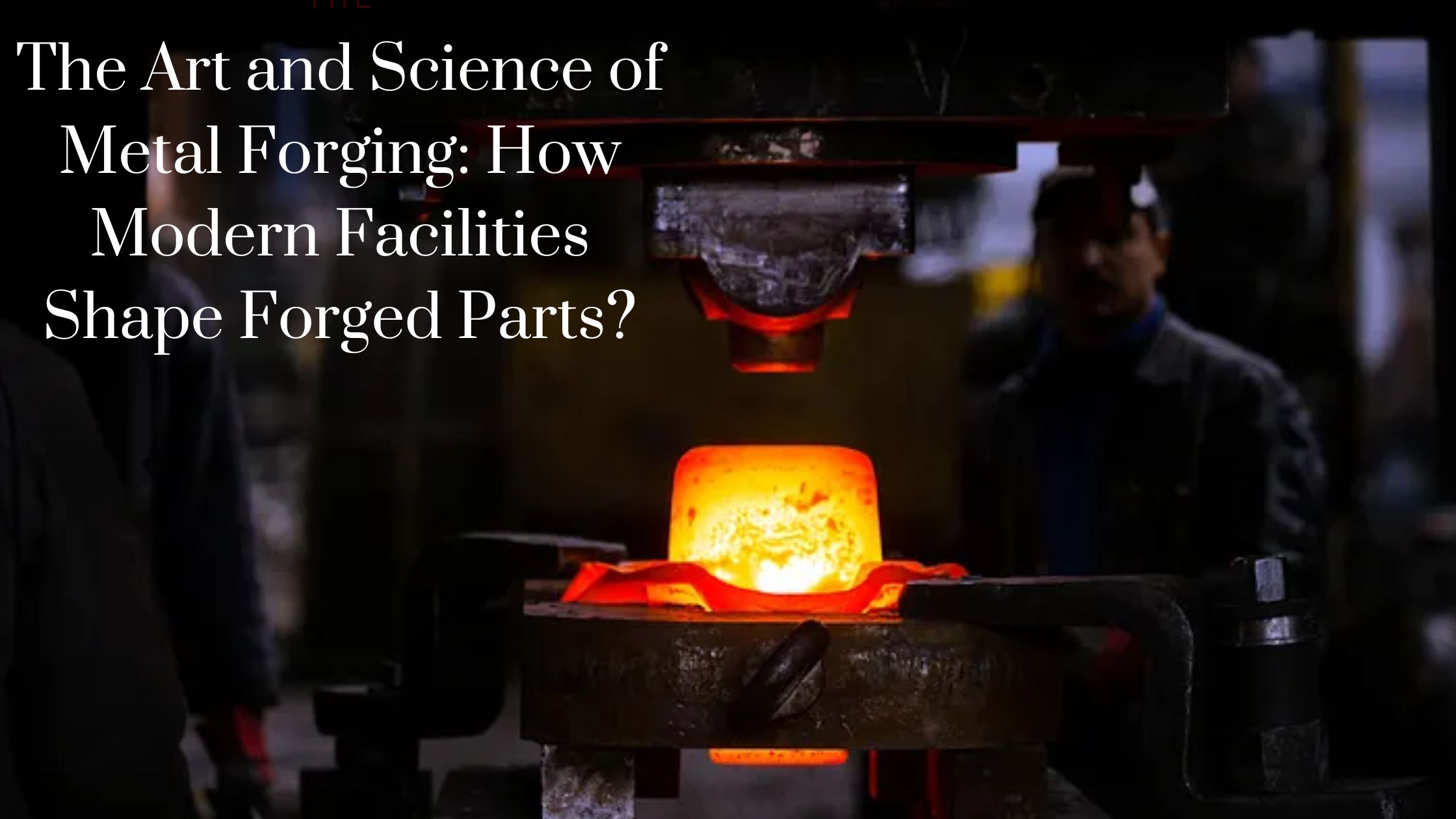
What exactly is forging?
Manufacturing is a procedure that includes shaping a metal by thrashing, pressing, or rolling it. Forging is one of the industrial techniques where hammer or die is utilized to apply such compressive pressures to the material beneath. Cold forging, warm, and hot forging are the three quite common categorizations for forging.
Forging is a process which normally includes the usage of metals like carbon steel, alloy steel, and stainless steel. The practice of forging might also be used to make soft metals such as copper, brass, and aluminum. Steel may be forged from a wide-ranging variety of metals.
The technique of forging may create components with exceptional mechanical qualities while generating a minimal amount of waste. The fundamental idea is that the original metal is plastically deformed into the required geometric shape, which results in the metal having increased fatigue resistance and strength. The method is one that is not only economically viable but also has the capacity to manufacture components in large quantities and to obtain certain mechanical qualities in the final product.
The unique benefits depending on the end product’s provisions. The materials forged could range from steel and aluminum to titanium and copper, broadening the scope of businesses that advantage from this multipurpose manufacturing procedure automotive, aerospace, construction, and more.
Understanding the process of forging?
- Forging is a wide process that may be broken down into several subtypes; hence, the specific stages that are involved in the formation of a product might vary. The majority of processes, on the other hand, will adhere to the same fundamental framework.
- As a result of the fact that forging is dependent on the utilization of dies to compress and shape metal, it is essential to ascertain which collection of tools will be the most efficient in order to accomplish the intended form. In many instances, the creation of a custom die will be required in order to guarantee that the finished product will be in perfect accordance with the specifications. It is possible that this stage will include the design and fabrication of various dies that are intended for flattening, shaping, or cutting depending on the size of the production run.
- You can begin the actual metalworking process after the planning and tool making processes have been finished. To begin, the workpiece or billet must be cut to the appropriate dimensions. It is necessary to heat it to the appropriate temperature once it has been cut. It is now possible to shape the billet after it has been heated.
- There is a beginning of divergence between the different forging procedures at this time. The billet may be heated and crushed between two dies, or it may be put into a molded chamber and compacted. This is determined by the technique that is used. A technique known as cold forging is used in some circumstances, in which the operator will let the billet to remain at room temperature and then manually manipulate it with hammers.
- Last but not least, there can be certain finishing operations that are required. To provide one example, some dies will create flashing that has to be cut afterwards.
The following are some additional advantages of forging:
1. Tensile strength
According to the findings of a research conducted by the University of Toledo, the tensile strength of forged components was 26% greater than that of identical cast-iron components. As a consequence of this, forged components are able to endure a much greater amount of stress without ripping than other parts.
2. Strength
Machineries that have been forged have been
shown to have an amazing strength, which allows them to have a lengthier
working life associated to components that have been made using other processes
when they are considered in the same heavy-duty functioning situations.
3. Versatility
Casting and forging are two ways which might be
used to manufacture extensive variety of items, both big and small. There are
very few instances in which casting is preferable than forging for the purpose
of getting a new shape.
4. Uniformity
Forged components have a more homogeneous content and structure than cast components, which adds to their amazing working life. Cast components have a more uniform composition and structure.
Bottom Line
Forged components are the epitome of strength, accuracy, and longevity in their highest form. Their influence cannot be refuted, stemming from the one-of-a-kind qualities that are the product of the forging process as well as the many benefits that they provide to a variety of different businesses. As technological and methodological advancements continue to be made, the journey of forging foundries India components also continues to change, incorporating innovation and excellence into the very fabric of contemporary production.




