Do you know?
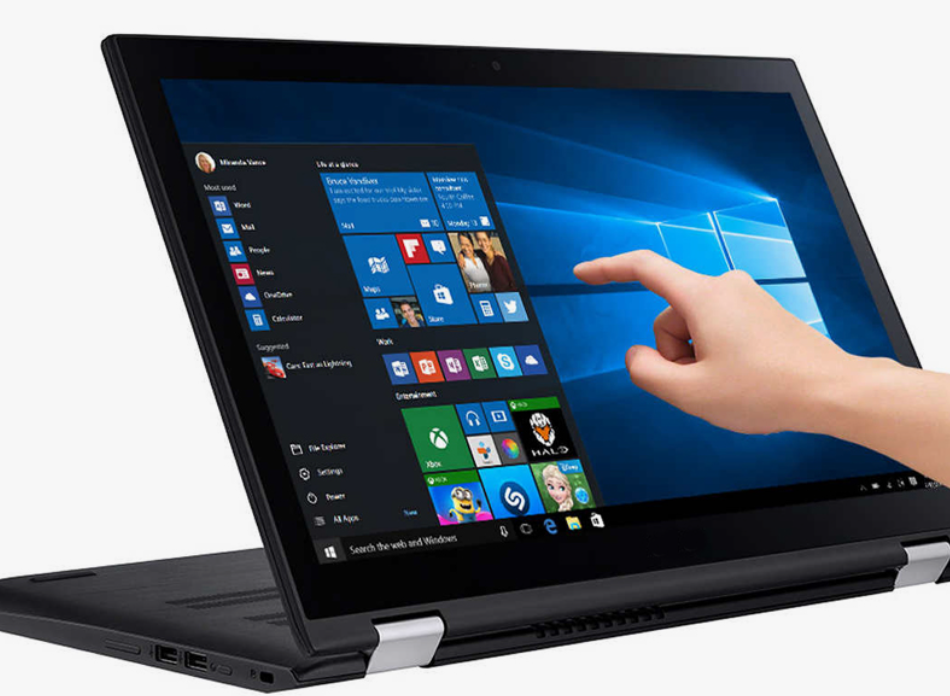
The global touchscreen laptop market, valued at USD 4.39 billion in 2023, is projected to reach USD 10.01 billion by 2030. This growth corresponds to a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12.5% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2030.
This data shows how touchscreen displays are becoming a bigger part of our daily lives. Whether it’s swiping through social media, zooming in on photos, or using a virtual keyboard, touchscreens are now a common part of how we use technology.
But have you ever stopped to wonder what makes these screens so intuitive and responsive?
With the growing use of touchscreen technology in laptops and other devices, it’s essential to know about the technology that powers these displays. Understanding this process highlights the complexity and effectiveness behind their functionality.
Continuing this discussion,
Let’s explore five key technologies behind touchscreen laptop displays, uncovering the magic that happens each time you touch, swipe, or pinch on the screen.
1. Capacitive Touchscreen Technology
Capacitive touchscreens are widely used in modern laptops due to their accuracy and responsiveness. These screens work by detecting the electrical charge from your finger, which is a conductor of electricity.
For instance: in an i5 touchscreen laptop, when you touch the screen, it distorts the electric field, and the system detects this change. This allows the laptop to register multiple touchpoints simultaneously, enabling smooth and precise gestures such as pinch-to-zoom, swiping, and rotating.
According to a write by tech target:
“A capacitive touchscreen is a control display that uses the conductive touch of a human finger or a specialized input device for input and control”.
Key Features of Capacitive Screens:
- High Sensitivity: Requires minimal pressure, making the display more responsive.
- Multi-touch Support: This enables handling complex gestures like multi-finger pinch, swipe, and zoom.
- Durability: Less susceptible to wear, as the screen doesn’t rely on physical pressure but electrical conductivity.
Capacitive touchscreens are favored for their high accuracy, responsiveness, and clarity.
Their ability to support multi-touch makes them ideal for advanced user interfaces and high-performance laptop experiences.
2. Resistive Touchscreen
In contrast to capacitive touchscreens, resistive touchscreens rely on pressure rather than electrical conductivity. These screens are composed of multiple layers, including a flexible, transparent layer that covers the display.
When pressure is applied, the screen’s layers make contact, and the device registers the input. This technology is less common in modern laptops but is often used in devices where precise input is needed, such as in industrial applications.
Key Features of Resistive Screens:
- Pressure Sensitivity: Works well with stylus input, making it useful for design and drawing applications.
- Durability: Can withstand rough usage, as they are less sensitive to environmental factors.
- Lower Cost: Generally cheaper to manufacture compared to capacitive touchscreens.
While resistive touchscreens don’t offer the smooth, multi-touch experience of capacitive screens, they remain a practical solution for certain use cases.
3. Infrared (IR) Touch Technology
Infrared touchscreens work by using a grid of infrared light beams across the screen. Sensors at the corners of the display send out infrared light that creates an invisible grid on the surface of the screen.
According to one of the reports,
The global infrared touch panel market was valued at approximately USD 4.5 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 7.8%, reaching an estimated USD 8.8 billion by 2032.
When a user’s finger or stylus interrupts the infrared beams, the system can detect the precise location of the touch. Infrared touch technology is highly accurate and works without making direct contact with the surface of the screen.
Key Features of Infrared Touchscreens:
- No Physical Layer: Unlike capacitive or resistive screens, infrared touchscreens don’t have physical layers that wear out over time.
- Multi-touch Support: Can detect multiple points of contact, enabling multi-finger gestures and interactions.
- High Clarity: Because there is no need for an additional layer, IR screens can offer excellent clarity and vibrant colors.
4. Optical Imaging Technology
Optical imaging technology uses cameras and infrared sensors to detect touch. A system of cameras placed around the screen captures the movement of light emitted by the user’s fingers or stylus.
The sensors then triangulate the position of the touch by analyzing the pattern of light interruption. This technology is often found in larger touchscreen displays, such as kiosks, but it’s also making its way into laptop screens.
Key Features of Optical Imaging Screens:
- High Accuracy: Can accurately detect the location of a touch without the need for direct contact.
- Durability: There are no physical layers to wear out, so optical imaging systems can last longer than other touchscreen technologies.
- Wide Coverage: Capable of supporting gestures with different types of input devices, such as hands, styluses, or even gloves.
While optical imaging technology isn’t as common in traditional laptops, it is gaining popularity for interactive displays and devices that require high-touch accuracy.
5. Surface Acoustic Wave (SAW)
Surface Acoustic Wave technology utilizes ultrasonic waves that travel across the screen’s surface.
When a finger or stylus touches the display, it absorbs the ultrasonic waves, causing a disruption in the system.
The market of SAW is continuously on the rise as mentioned in one of the reports by Linkedin, It states, “
“The Surface Acoustic Wave (SAW) Touch Screen Market, valued at USD 1.2 billion in 2022, is projected to reach USD 2.4 billion by 2030, with a 9.2% CAGR from 2024 to 2030”.
Sensors then detect the disruption and calculate the precise location of the touch. SAW technology is commonly used in public-facing devices, such as kiosks, but can also be found in some laptop touchscreens.
Key Features of SAW Technology:
- High Transparency: The technology doesn’t require any layers that would reduce the display’s clarity.
- No Physical Contact Required: Like infrared touchscreens, SAW displays don’t require pressure for operation, making them more durable.
- Resistant to Contamination: Since there are no physical layers on the screen, dust and dirt won’t affect the touch detection.
Despite being less commonly found in laptops, SAW technology offers several benefits, especially in environments where screen clarity and durability are critical.
Conclusion: Why These Technologies Matter
Each of the five touchscreen technologies plays a unique role in the evolution of laptop displays. Capacitive screens dominate the market due to their responsiveness and multi-touch capabilities, while resistive and infrared technologies find their niches in specialized applications. Optical imaging and SAW technologies, although less common in everyday laptops, offer distinct advantages in specific environments.
As touchscreen laptops continue to evolve, these underlying technologies will only become more refined, offering more intuitive ways to interact with their devices.
Whether you’re tapping, swiping, or zooming, it’s these key technologies that make the touchscreen experience seamless, responsive, and powerful.
Read more: 5 Reasons Why Intel Arc GPU Leads In Video Production Workflows